Publications
Oredered in reversed chronological order.
2025
-
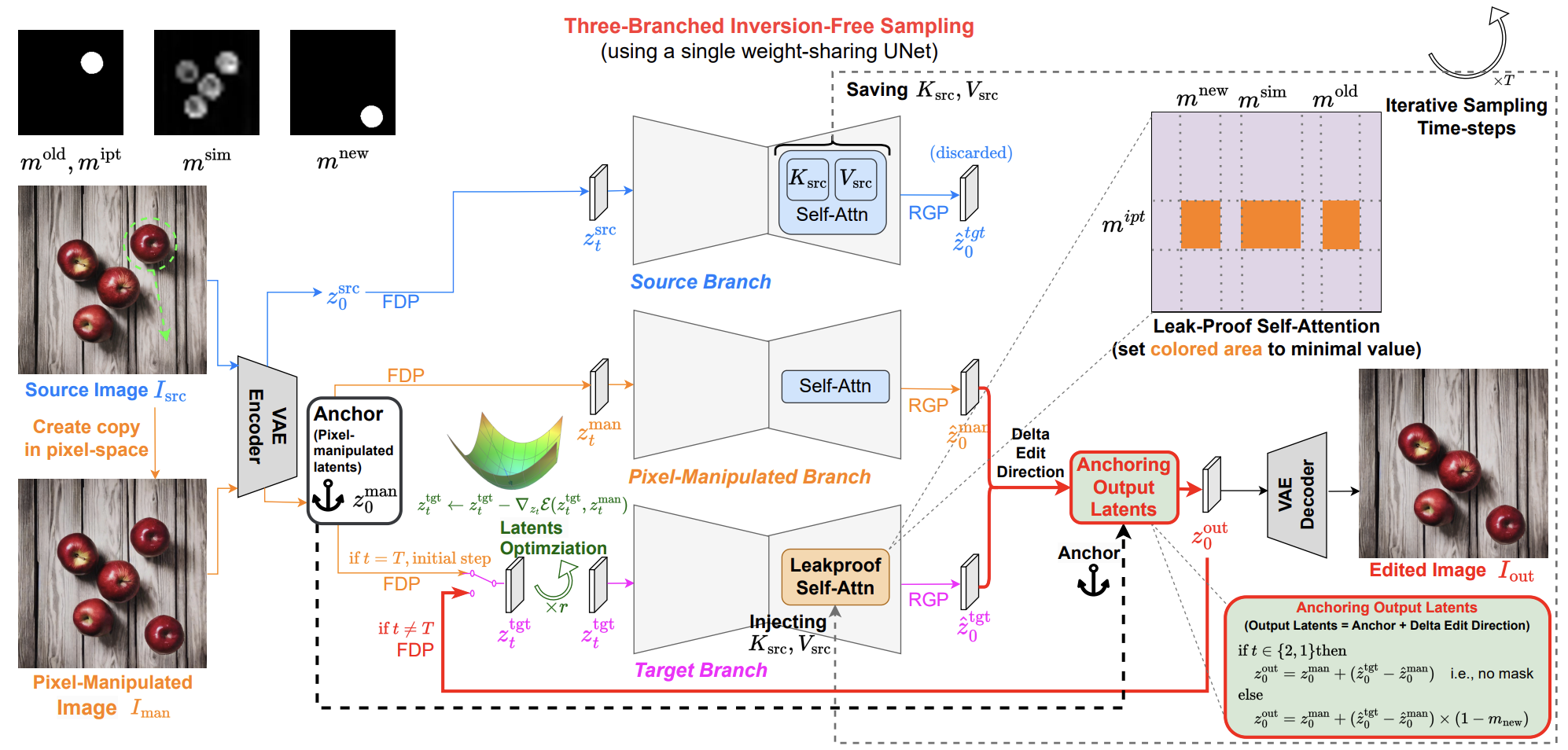 PixelMan: Consistent Object Editing with Diffusion Models via Pixel Manipulation and GenerationLiyao Jiang, Negar Hassanpour, Mohammad Salameh, and 4 more authorsThe 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2025
PixelMan: Consistent Object Editing with Diffusion Models via Pixel Manipulation and GenerationLiyao Jiang, Negar Hassanpour, Mohammad Salameh, and 4 more authorsThe 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2025Recent research explores the potential of Diffusion Models (DMs) for consistent object editing, which aims to modify object position, size, and composition, etc., while preserving the consistency of objects and background without changing their texture and attributes. Current inference-time methods often rely on DDIM inversion, which inherently compromises efficiency and the achievable consistency of edited images. Recent methods also utilize energy guidance which iteratively updates the predicted noise and can drive the latents away from the original image, resulting in distortions. In this paper, we propose PixelMan, an inversion-free and training-free method for achieving consistent object editing via Pixel Manipulation and generation, where we directly create a duplicate copy of the source object at target location in the pixel space, and introduce an efficient sampling approach to iteratively harmonize the manipulated object into the target location and inpaint its original location, while ensuring image consistency by anchoring the edited image to be generated to the pixel-manipulated image as well as by introducing various consistency-preserving optimization techniques during inference. Experimental evaluations based on benchmark datasets as well as extensive visual comparisons show that in as few as 16 inference steps, PixelMan outperforms a range of state-of-the-art training-based and training-free methods (usually requiring 50 steps) on multiple consistent object editing tasks.
-
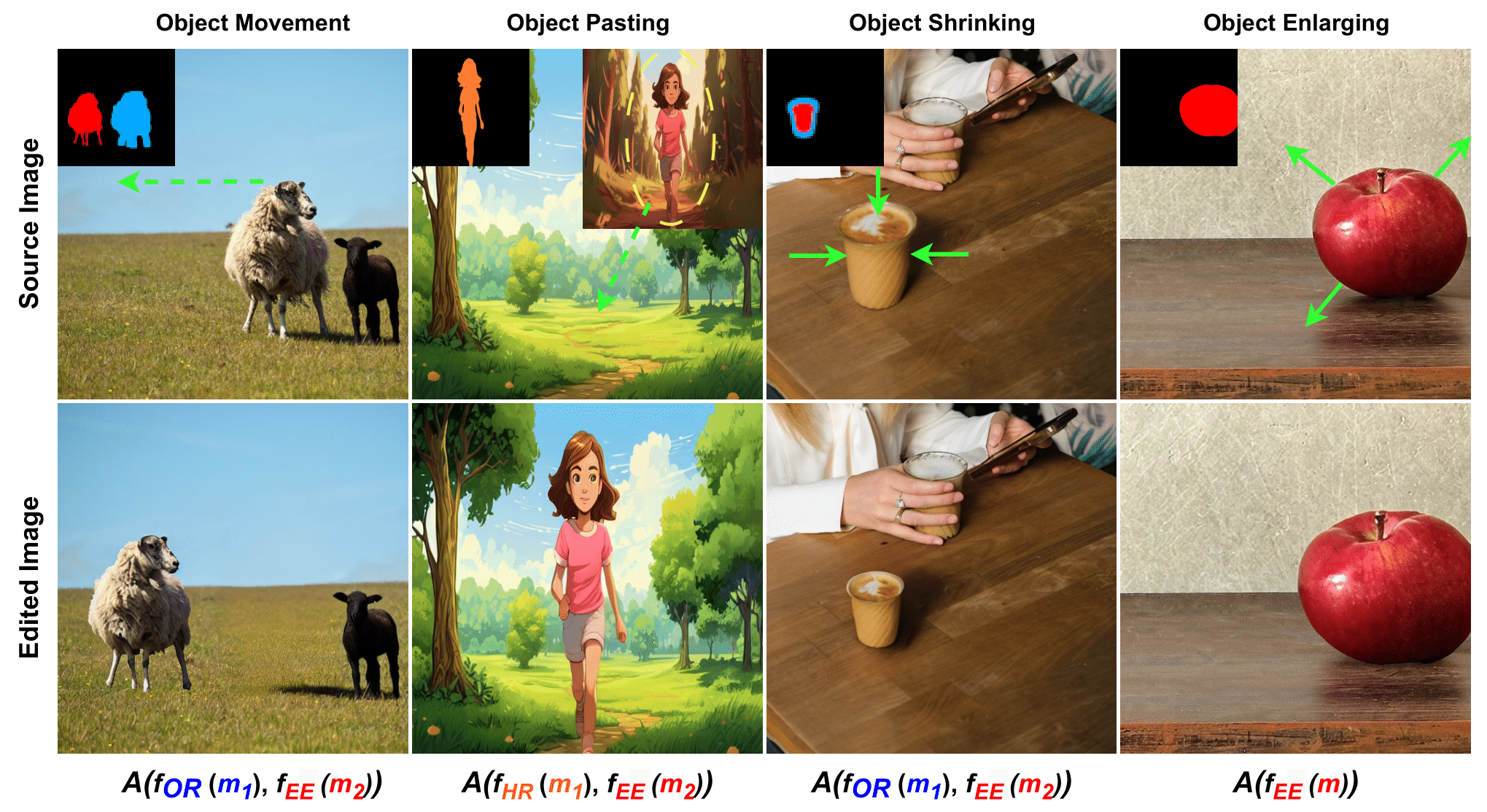 FunEditor: Achieving Complex Image Edits via Function Aggregation with Diffusion ModelsMohammadreza Samadi, Fred X Han, Mohammad Salameh, and 4 more authorsThe 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2025
FunEditor: Achieving Complex Image Edits via Function Aggregation with Diffusion ModelsMohammadreza Samadi, Fred X Han, Mohammad Salameh, and 4 more authorsThe 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2025Diffusion models have shown exceptional performance in generative tasks, making them suitable for image editing. Recent research highlights their ability to apply edits based on textual instructions, but two key challenges persist. First, these models struggle to perform multiple edits simultaneously, causing computational inefficiencies due to sequential processing. Second, using textual prompts to specify editing regions can result in unintended changes to the image. We introduce FunEditor, an efficient diffusion model designed to learn basic editing functions and combine them to perform complex edits. This method allows tasks like object movement by merging multiple functions and applying them simultaneously to designated areas. Our experiments show that FunEditor significantly outperforms recent inference-time optimization techniques and fine-tuned models, both quantitatively across various metrics and through visual comparisons, on complex tasks like object movement and object pasting. Moreover, with only four inference steps, FunEditor achieves a 5-24x speedup compared to existing popular methods. Codes and datasets are available online.
2023
-
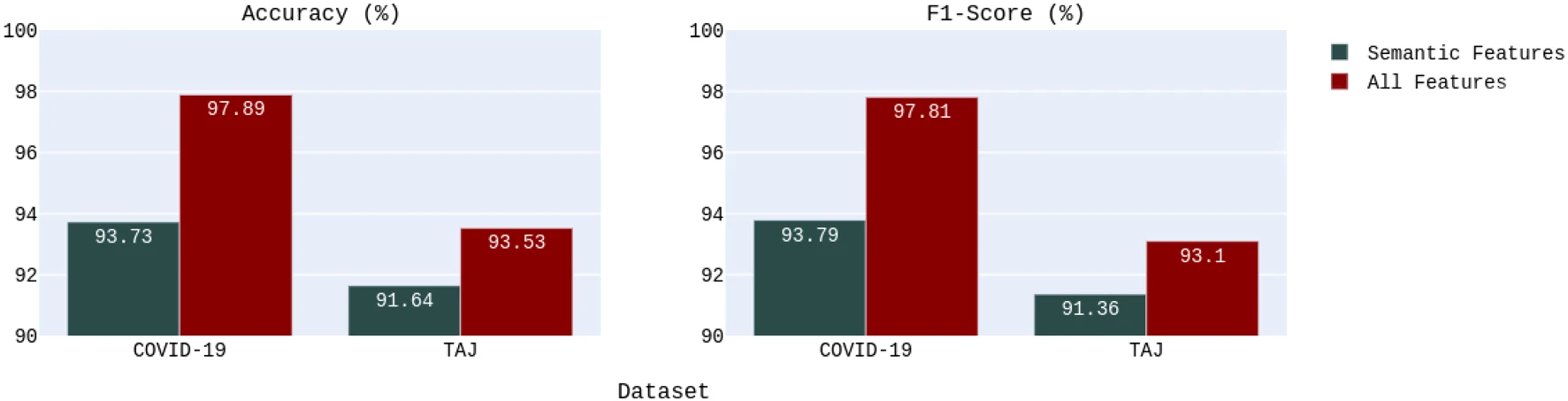 Fake news detection: deep semantic representation with enhanced feature engineeringMohammadreza Samadi, and Saeedeh MomtaziInternational Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2023
Fake news detection: deep semantic representation with enhanced feature engineeringMohammadreza Samadi, and Saeedeh MomtaziInternational Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2023Due to the widespread use of social media, people are exposed to fake news and misinformation. Spreading fake news has adverse effects on both the general public and governments. This issue motivated researchers to utilize advanced natural language processing concepts to detect such misinformation in social media. Despite the recent research studies that only focused on semantic features extracted by deep contextualized text representation models, we aim to show that content-based feature engineering can enhance the semantic models in a complex task like fake news detection. These features can provide valuable information from different aspects of input texts and assist our neural classifier in detecting fake and real news more accurately than using semantic features. To substantiate the effectiveness of feature engineering besides semantic features, we proposed a deep neural architecture in which three parallel convolutional neural network (CNN) layers extract semantic features from contextual representation vectors. Then, semantic and content-based features are fed to a fully connected layer. We evaluated our model on an English dataset about the COVID-19 pandemic and a domain-independent Persian fake news dataset (TAJ). Our experiments on the English COVID-19 dataset show 4.16% and 4.02% improvement in accuracy and f1-score, respectively, compared to the baseline model, which does not benefit from the content-based features. We also achieved 2.01% and 0.69% improvement in accuracy and f1-score, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art results reported by Shifath et al. (A transformer based approach for fighting covid-19 fake news, arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.12027, 2021). Our model outperformed the baseline on the TAJ dataset by improving accuracy and f1-score metrics by 1.89% and 1.74%, respectively. The model also shows 2.13% and 1.6% improvement in accuracy and f1-score, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art model proposed by Samadi et al.
-
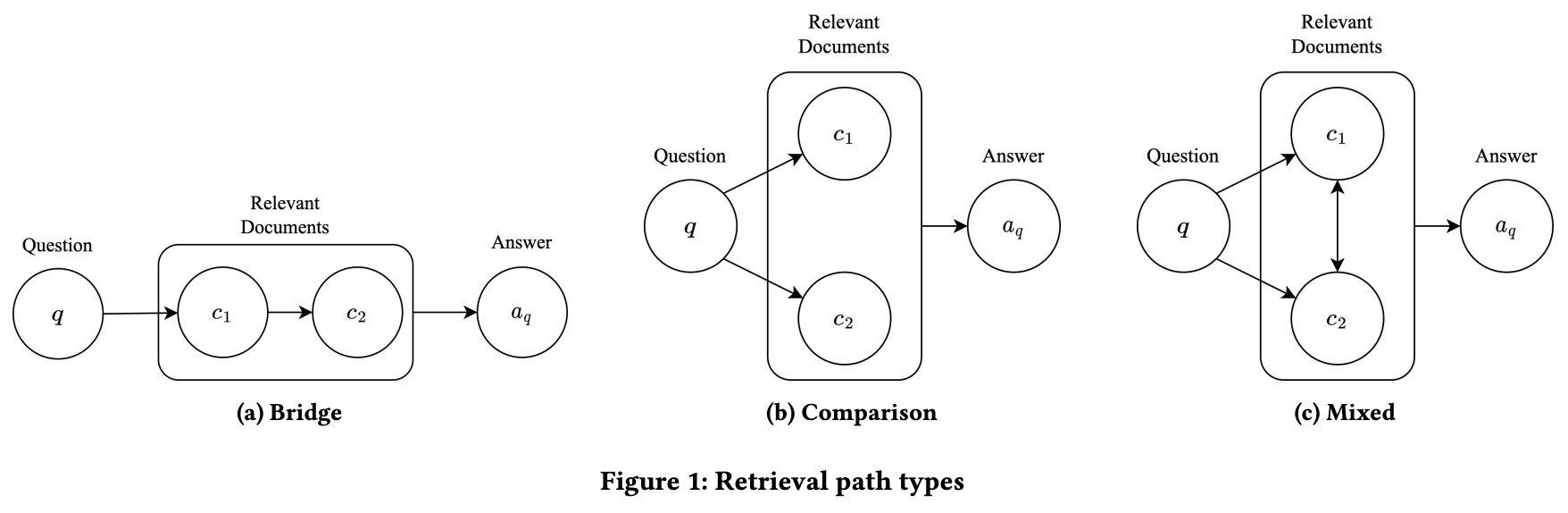 Performance Prediction for Multi-hop QuestionsMohammadreza Samadi, and Davood RafieiarXiv preprint arXiv:2308.06431, 2023
Performance Prediction for Multi-hop QuestionsMohammadreza Samadi, and Davood RafieiarXiv preprint arXiv:2308.06431, 2023We study the problem of Query Performance Prediction (QPP) for open-domain multi-hop Question Answering (QA), where the task is to estimate the difficulty of evaluating a multi-hop question over a corpus. Despite the extensive research on predicting the performance of ad-hoc and QA retrieval models, there has been a lack of study on the estimation of the difficulty of multi-hop questions. The problem is challenging due to the multi-step nature of the retrieval process, potential dependency of the steps and the reasoning involved. To tackle this challenge, we propose multHP, a novel pre-retrieval method for predicting the performance of open-domain multi-hop questions. Our extensive evaluation on the largest multi-hop QA dataset using several modern QA systems shows that the proposed model is a strong predictor of the performance, outperforming traditional single-hop QPP models. Additionally, we demonstrate that our approach can be effectively used to optimize the parameters of QA systems, such as the number of documents to be retrieved, resulting in improved overall retrieval performance.
2022
-
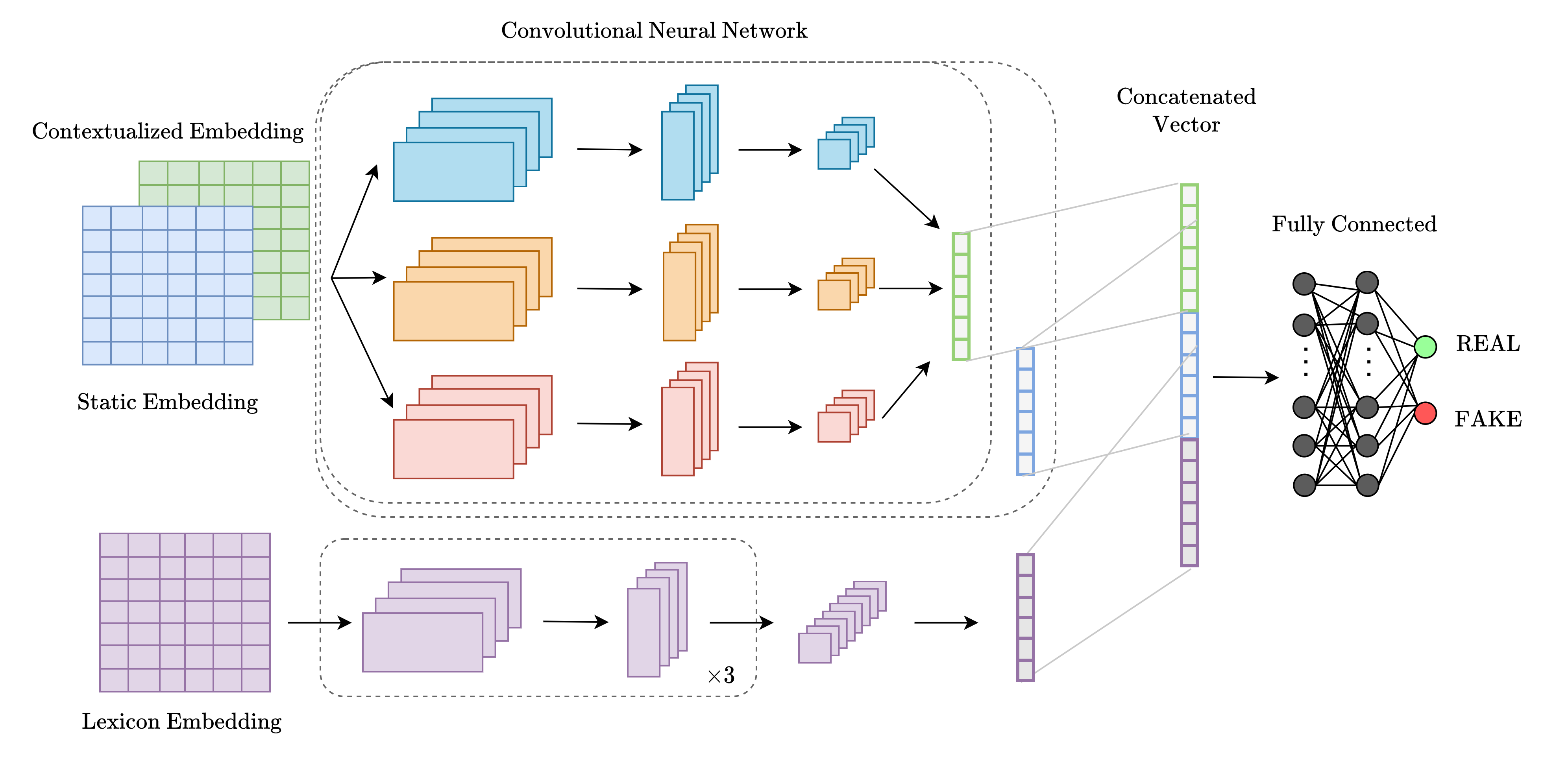 Multichannel convolutional neural networks for detecting COVID-19 fake newsMohammadreza Samadi, and Saeedeh MomtaziDigital Scholarship in the Humanities, 2022
Multichannel convolutional neural networks for detecting COVID-19 fake newsMohammadreza Samadi, and Saeedeh MomtaziDigital Scholarship in the Humanities, 2022By the outbreak of COVID-19, started in late 2019, people have been exposed to false information that not only made them confused about the scientific aspects of this virus but also endangered their life. This makes fake news detection a critical issue in social media. In this paper, we introduce a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based model for detecting fake news spread in social media. Considering the complexity of the fake news detection task, various features from different aspects of news articles should be captured. To this aim, we propose a multi-channel CNN model that uses three distinct embedding channels: (1) contextualized text representation models, (2) static word embeddings, and (3) lexical embeddings, all of which assist the classifier to detect fake news more accurately. Our experimental results on the COVID-19 fake news dataset (Patwa et al., 2020) shows that the CNN model with contextualized text representation improves the performance of the task by 2.96% compared to the reported results by Patwa et al. (2020). Moreover, our proposed three-channel CNN further improved the results by 0.56 % and 1.32 % on the validation and test data, respectively.
2021
-
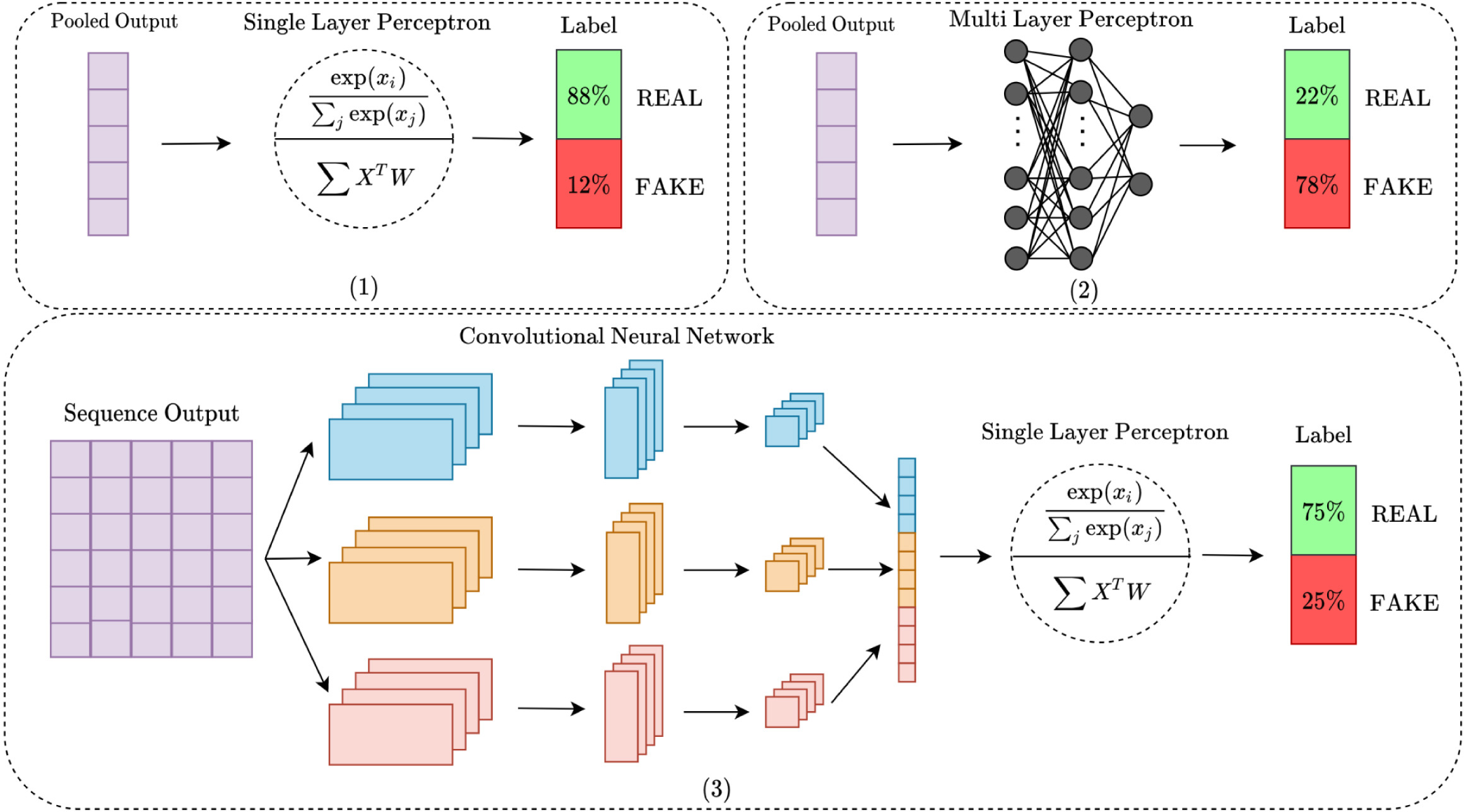 Deep contextualized text representation and learning for fake news detectionMohammadreza Samadi, Maryam Mousavian, and Saeedeh MomtaziInformation Processing & Management, 2021
Deep contextualized text representation and learning for fake news detectionMohammadreza Samadi, Maryam Mousavian, and Saeedeh MomtaziInformation Processing & Management, 2021In recent years, due to the widespread use of social media and broadcasting agencies around the world, people are extremely exposed to being affected by false information and fake news, all of which have negative impacts on both collective thoughts and governments’ policies. In recent years, the great success of pre-trained models for embedding contextual information from texts motivates researchers to utilize these embeddings in different natural language processing tasks. However, in a complex task like fake news detection, it is not determined which contextualized embedding can assist the classifier with more valuable features. Due to the lack of a comparative study about utilizing different contextualized pre-trained models besides distinct neural classifiers, we aim to dive into a comparative study about using different classifiers and embedding models. In this paper, we propose three classifiers with different pre-trained models for embedding input news articles. We connect Single-Layer Perceptron (SLP), Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) after the embedding layer which consists of novel pre-trained models such as BERT, RoBERTa, GPT2, and Funnel Transformer in order to benefit from deep contextualized representation provided by those models as well as deep neural classifications. We evaluate our proposed models on three well-known fake news datasets: LIAR (Wang, 2017), ISOT (Ahmed et al., 2017), and COVID-19 Patwa et al. (2020). The results on these three datasets show the superiority of our proposed models for fake news detection compared to the state-of-the-art models. The results show 7% and 0.1% improvements in classification accuracy compared to the proposed model by Goldani et al. (2021) on LIAR and ISOT, respectively. We also achieved 1% improvement compared to the proposed model by Shifath et al. (2021) on the COVID-19 dataset.
-
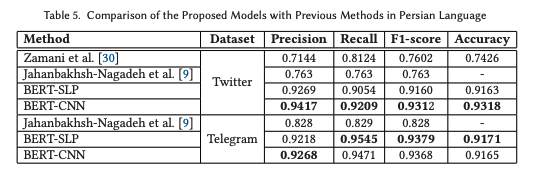 Persian fake news detection: Neural representation and classification at word and text levelsMohammadreza Samadi, Maryam Mousavian, and Saeedeh MomtaziTransactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 2021
Persian fake news detection: Neural representation and classification at word and text levelsMohammadreza Samadi, Maryam Mousavian, and Saeedeh MomtaziTransactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 2021Nowadays, broadcasting news on social media and websites has grown at a swifter pace, which has had negative impacts on both the general public and governments; hence, this has urged us to build a fake news detection system. Contextualized word embeddings have achieved great success in recent years due to their power to embed both syntactic and semantic features of textual contents. In this article, we aim to address the problem of the lack of fake news datasets in Persian by introducing a new dataset crawled from different news agencies, and propose two deep models based on the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers model (BERT), which is a deep contextualized pre-trained model for extracting valuable features. In our proposed models, we benefit from two different settings of BERT, namely pool-based representation, which provides a representation for the whole document, and sequence representation, which provides a representation for each token of the document. In the former one, we connect a Single Layer Perceptron (SLP) to the BERT to use the embedding directly for detecting fake news. The latter one uses Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) after the BERT’s embedding layer to extract extra features based on the collocation of words in a corpus. Furthermore, we present the TAJ dataset, which is a new Persian fake news dataset crawled from news agencies’ websites. We evaluate our proposed models on the newly provided TAJ dataset as well as the two different Persian rumor datasets as baselines. The results indicate the effectiveness of using deep contextualized embedding approaches for the fake news detection task. We also show that both BERT-SLP and BERT-CNN models achieve superior performance to the previous baselines and traditional machine learning models, with 15.58% and 17.1% improvement compared to the reported results by Zamani et al. [30], and 11.29% and 11.18% improvement compared to the reported results by Jahanbakhsh-Nagadeh et al. [9].
-
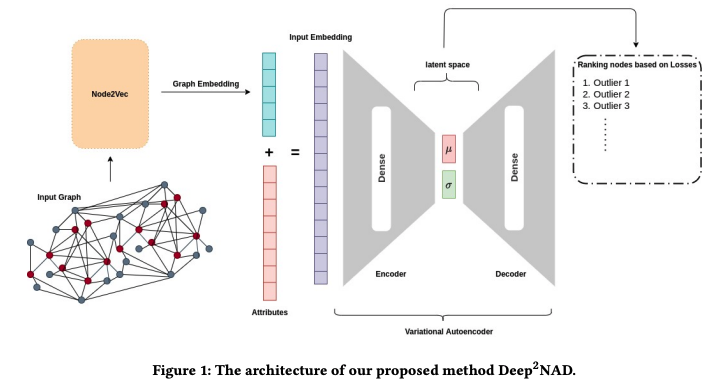 Unsupervised Anomaly Detection on Node Attributed Networks: A Deep Learning ApproachParsa Kavehzadeh, Mohammadreza Samadi, and Maryam Amir HaeriIn 2021 The 4th International Conference on Information Science and Systems, 2021
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection on Node Attributed Networks: A Deep Learning ApproachParsa Kavehzadeh, Mohammadreza Samadi, and Maryam Amir HaeriIn 2021 The 4th International Conference on Information Science and Systems, 2021Anomaly detection has been one of the important issues in social network analysis in recent years due to the crucial role it plays in different applications such as fraud and spammer detection. Using both graph and node characteristics leads to more accurate results in detecting anomalous nodes of node attributed networks. Most of the research works in this field are concentrated on supervised methods for anomaly detection. However, in real-world problems, there is not enough labeled data to use supervised methods for anomaly detection. This paper proposes an unsupervised method for detecting anomalous nodes in node attributed networks. The methods used a two-step deep learning approach. In the first step, structural features of the network are extracted using node2vec; in the next step, Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) is used to detect the anomalies considering both structural and node attributes. The anomalous nodes are recognized by their higher reconstruction loss. Our experimental results on two datasets, BlogCatalog and Flickr, show that the suggested method can compete with the state-of-the-art approaches of anomaly detection in attributed networks. Our method (Deep2NAD) outperforms the state-of-the-art result on the Flickr dataset based on AUC. Moreover, it receives an acceptable AUC over the BlogCatalog dataset in comparison to the state-of-the-art methods.